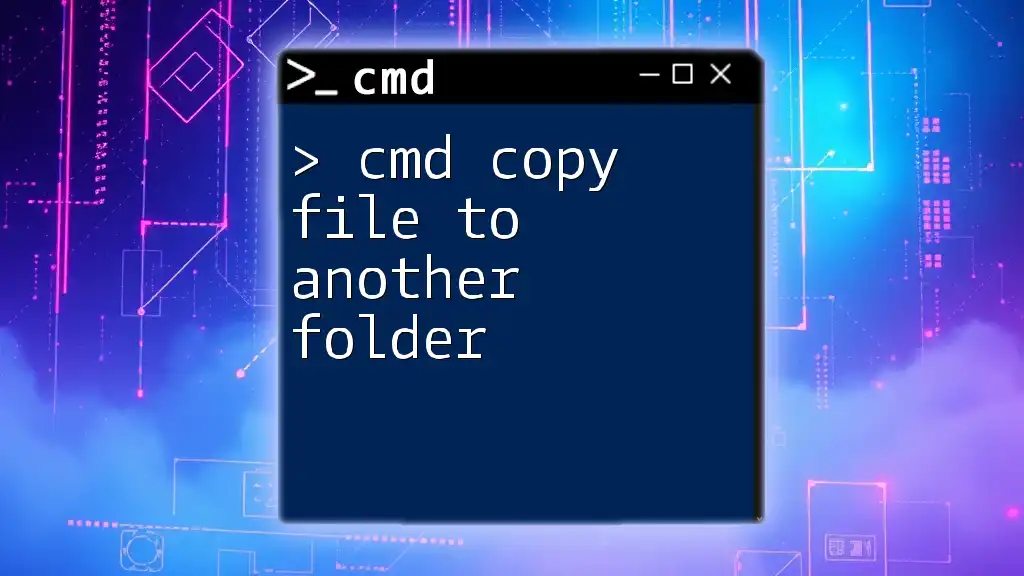
To copy a file from one folder to another using CMD, you can use the `copy` command followed by the source file path and the destination folder path. Here's a code snippet demonstrating this:
copy C:\path\to\source\file.txt D:\path\to\destination\
Understanding CMD and File Operations
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interpreter available in Windows operating systems. It allows users to execute commands to perform various administrative tasks. CMD provides a powerful way to interact with the file system and manipulate files and directories directly through textual commands.
Basic File Operations
In the context of file management, CMD offers functionalities to perform a variety of operations, including creating, deleting, copying, and moving files. The copy command specifically is essential for duplicating files and transferring them from one location to another without removing the original files.

The Copy Command in CMD
Syntax of the Copy Command
The basic syntax of the copy command is:
copy [source] [destination]
- [source]: the path and name of the file you want to copy.
- [destination]: the path where you want to place the copied file.
Basic Example of Copying Files
To begin using the copy command, here's a straightforward example of copying a single text file from one folder to another:
copy C:\source\file.txt D:\destination\
In this example:
- `C:\source\file.txt` is the file you wish to copy.
- `D:\destination\` is the destination folder where the file will be copied.
- Upon executing this command, a duplicate of file.txt will appear in the specified destination folder.

Copying Multiple Files
Using Wildcards
Wildcards are helpful when you want to copy multiple files matching a specific pattern. The asterisk (*) represents zero or more characters, and the question mark (?) stands for a single character.
For example:
copy C:\source\*.txt D:\destination\
In this scenario:
- All `.txt` files located in the source folder are copied to the destination folder.
- This is a quick way to transfer multiple files without specifying each one individually.
Specifying Multiple Files
If you need to copy multiple specific files that are not in a sequence, you can list them in the command:
copy C:\source\file1.txt C:\source\file2.txt D:\destination\
In this example:
- Two files, file1.txt and file2.txt, are individually copied to the destination folder.
- Ensure that each specified file path is correct to avoid errors.

Copying Folders and Their Contents
Using the Xcopy Command
For copying entire folders, the `xcopy` command is more suitable due to its advanced options. Here's how to use it:
xcopy C:\source\folder D:\destination\ /E /I
Breaking it down:
- /E copies all files and subdirectories, including empty ones.
- /I specifies that the destination is a directory if it does not exist.
- This command preserves the structure of the source and transfers everything within it.
Using the Robocopy Command
For more complex and large file copying tasks, the `robocopy` command is an industry-standard choice. Here's a basic example:
robocopy C:\source D:\destination /E
Key features of `robocopy` include:
- Robust error handling and the ability to resume broken file transfers.
- The /E option, which copies all files and folders, including empty directories.
- It is particularly powerful for handling large datasets or multiple file transfers.

Common Errors and Troubleshooting
Handling File Not Found Errors
One of the most common errors when using the copy command is the File Not Found error. This typically arises when the specified source path or file name is incorrect. Here are some solutions:
- Double-check the path and file names for typos or incorrect characters.
- Ensure the file actually exists in the specified location.
Access Denied and Permissions Issues
Upon attempting to copy files, you may encounter Access Denied messages. This often indicates insufficient permissions to access the file or destination folder. To resolve this:
- Run CMD as an administrator by right-clicking on the Command Prompt icon and selecting "Run as administrator."
- Verify the permissions on the file or folder and make necessary adjustments.
Target Directory Issues
Sometimes the target directory is incorrect or doesn't exist. Ensure that the specified destination path is valid, and, if necessary, create the directory first using the `mkdir` command:
mkdir D:\destination
Conclusion
In summary, the cmd copy file to another folder command is a vital skill for any user looking to enhance their file management proficiency. Whether you're copying individual files, multiple files, or even entire folders, mastering these CMD commands can significantly streamline your workflow. Practice using these commands to become more effective in managing your files and utilities with CMD.
FAQs
Can I copy files from a network folder?
Yes, you can use the copy command to move files from a network folder as long as you have the correct network path and the requisite permissions.
What should I do if I need to overwrite existing files?
To allow overwriting existing files, you can simply run the copy command as usual. CMD will prompt you for confirmation if the files have the same name. To suppress overwrite prompts, use the `/-Y` option.
How can I copy hidden files?
To include hidden files in your copying operations, ensure you use the `/H` option with either the copy, xcopy, or robocopy commands. For example:
xcopy C:\source D:\destination /E /H
This will ensure hidden files are also copied over to the destination.

Additional Resources
For more CMD commands and tutorials, consider exploring additional educational materials that deepen your understanding of Command Prompt functionalities. Practice is key to mastering these powerful tools!