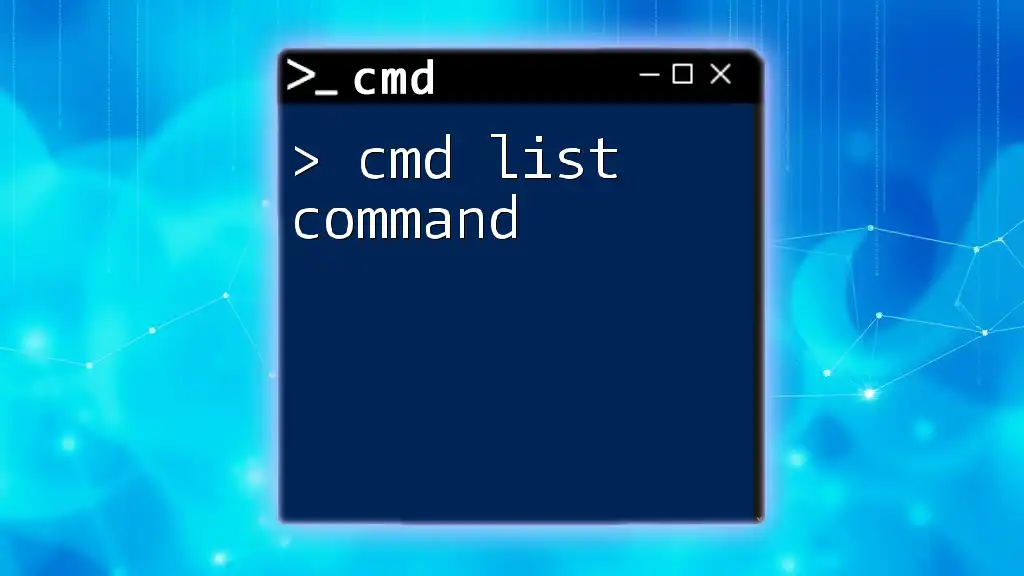
The `chkdsk` command in CMD is used to check the integrity of a disk and fix logical file system errors.
Here's how you can use it:
chkdsk C: /f
This command checks the C: drive and automatically fixes any found errors.
Understanding the Disk Check Command
What is the Disk Check Command?
The cmd disk check command is a vital tool used for maintaining the integrity of your disk drives. It allows users to verify the file system and file system metadata of a volume, ensuring that the operating system runs smoothly. Regular disk checks can prevent data corruption and enhance system performance, thereby extending the lifespan of your hard drive or SSD.
Introducing the CHKDSK Command
The command utilized for this purpose is CHKDSK, short for "Check Disk." This command scans the drive for issues and can often fix these problems on-the-fly. The `chkdsk command cmd` is especially useful when the system experiences crashes, unexpected shutdowns, or if it detects file system errors. Through the command line, users can easily run diagnostics and repairs to maintain their computer's health.

How to Access the Command Prompt
Opening Command Prompt
Accessing the Command Prompt is straightforward. There are several methods through which you can launch the `cmd`:
- Using the Run Dialog: Press `Windows + R`, type `cmd`, and hit Enter.
- Start Menu: Click on the Start button, type "cmd" or "Command Prompt," and select the application.
- Windows Search: Click on the magnifying glass icon in your taskbar, type "cmd," and press Enter.
Navigating the Command Prompt
Once in the Command Prompt, you can navigate using various commands like `cd` (change directory) and `dir` (display the contents of a directory). Familiarity with these basic commands helps in efficiently executing the disk check command.

Using the CHKDSK Command
Syntax of the CHKDSK Command
The syntax for the CHKDSK command is as follows:
chkdsk [volume:][[path] filename] [/f] [/r] [/x] [/v] [/scan]
Here, [volume:] refers to the drive letter, such as `C:` for the primary drive, and the parameters specify how the command will function.
Explanation of Command Parameters
Common Parameters
- /f: This option tells CHKDSK to fix any errors it finds on the disk. It's crucial for repairing damaged file systems.
- /r: This parameter not only fixes file system errors but also locates bad sectors on the disk and recovers any readable information.
- /x: This forces the volume to dismount first, which is helpful if the drive is in use by another process.
- /v: Provides a detailed list of filenames during the check, giving the user a comprehensive overview.
- /scan: Scans the volume for problems without performing repairs.
Example Commands
Basic Disk Check
To perform a simple disk check, you would enter:
chkdsk C:
This command initiates a scan on the C: drive and provides basic information about any errors detected.
Fixing Disk Errors
To fix any detected file system errors, append the `/f` flag:
chkdsk C: /f
This command automatically repairs issues, which is essential for maintaining system robustness.
Scanning with Details
If you want a detailed report during your disk exercise, use the `/v` flag:
chkdsk D: /v
This command will not only check the disk but will also present a list of all files in the affected sectors, providing insight into what’s going on.

Advanced Usage of CHKDSK
Running CHKDSK on Boot Time
Sometimes, CHKDSK needs to perform repairs that require the drive to be inactive. To achieve this, you can run:
chkdsk C: /f /r
If the drive is in use, Windows will prompt you to schedule this command for the next reboot. This method ensures that all repairs are made before the operating system loads.
Scheduling a Disk Check
To schedule CHKDSK for the next system start, you can incorporate the `/f` and `/r` flags as indicated above. The system will execute the scan and necessary repairs on the next boot, ensuring a clean slate for your drive.

Checking Disk Health
Using SMART Attributes
SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) is another tool to assess disk health. Though not directly a `cmd` command, incorporating `cmd` commands with third-party SMART analysis tools provides deeper insights into the drive's condition. While `chkdsk` focuses on errors from file processes, SMART checks the physical state of the drive, identifying imminent drive failures.
Third-Party Tools vs. Built-in CMD
While CHKDSK is an excellent tool for maintaining your disk's health, several third-party applications offer more advanced features. They can present visual analyses, perform benchmarking, and provide scheduled tasks without user intervention. However, using built-in CMD commands has unique advantages: they require no additional software and are integrated directly into Windows.

Troubleshooting Common Issues
What to Do When CHKDSK Fails
Even reliable commands like CHKDSK can occasionally encounter issues and return error messages. Common problems may include disk corruption or parameters that might be incorrectly set. To troubleshoot:
- Review Error Messages: Identifying the specific error can guide you towards solutions.
- Log Files: Redirect output to a text file for later review:
This command logs the results of your disk check, allowing you to analyze the output more thoroughly.chkdsk C: > C:\chkdsk_log.txt

Conclusion
Using the cmd disk check command is essential for maintaining the health and performance of your disk drives. The CHKDSK command offers a reliable means of checking and repairing your file systems, ensuring that potential issues are addressed before they escalate into more significant problems. Regularly utilizing this command will help optimize your computer’s performance and prolong the lifespan of your storage devices.

Additional Resources
Links to Further Readings
To further enhance your understanding of the CHKDSK tool, you can refer to Microsoft’s official documentation or other specialized resources on CMD commands.
Join Our Community
We invite you to join our community for more tips and tricks on using CMD effectively. Share your experiences, ask questions, and enjoy learning how to optimize your system through command line usage!