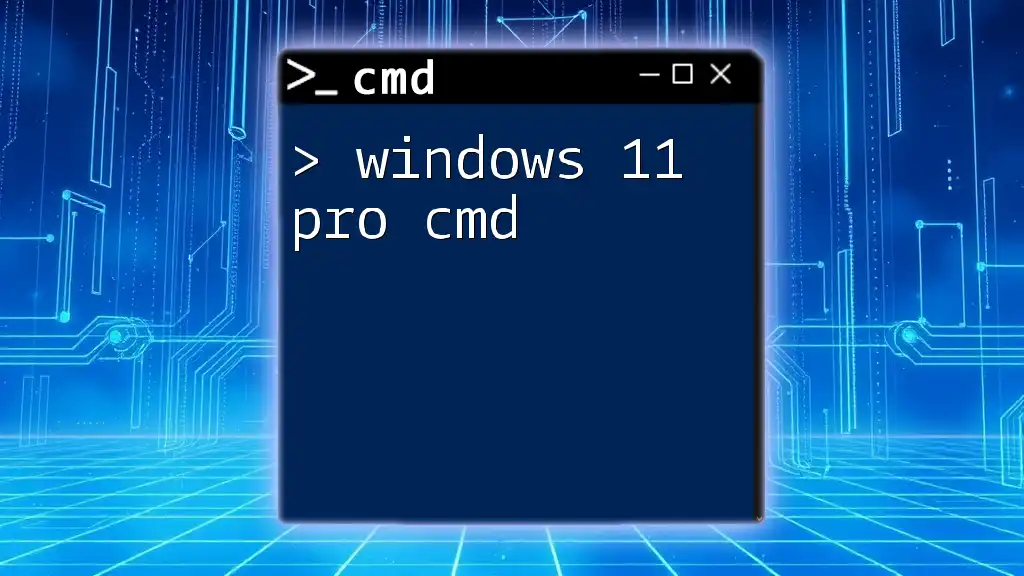
To skip setting up a Microsoft account during Windows 10 installation using CMD, you can utilize the following command in the Windows Command Prompt.
OOBE /BYPASSNRO
Understanding Microsoft Accounts versus Local Accounts
What is a Microsoft Account?
A Microsoft account is a single sign-on account that allows users to access various Microsoft services and products, such as Outlook, OneDrive, and the Microsoft Store. It brings several features such as:
- Cloud Integration: Seamlessly sync settings, files, and preferences across different devices.
- Security Features: Enhanced security options like two-factor authentication.
- Access to Microsoft Services: Direct access to Windows Store, Xbox Live, and other Microsoft platforms.
While Microsoft accounts provide these benefits, not all users find them necessary. It’s essential to assess the need for such integration versus the preference for more straightforward, offline access.
What is a Local Account?
A local account, as the name implies, resides on your device rather than being linked or managed online. Key characteristics include:
- Privacy: Local accounts do not send data back to Microsoft, enhancing user privacy.
- Simplicity: A straightforward login without the complexities of the online account management systems.
- Offline Usability: Ideal for users who prioritize local storage and do not need the features associated with a Microsoft account.
Choosing a local account can be especially useful for those who do not require the additional functionalities provided by Microsoft's services.
Why Skip Microsoft Account Setup?
Benefits of Skipping the Microsoft Account
Bypassing the Microsoft account setup can lead to numerous benefits. Here are a few:
- Increased Privacy: Users can feel more secure knowing their data is not being stored in Microsoft's ecosystem.
- Simplicity for Users: For those who prefer a straightforward computing experience, local accounts eliminate unnecessary prompts and complexities during setup.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Data Syncing: Users can manage their files locally without grappling with cloud storage or syncing settings.
Scenarios for Skipping
Several situations may warrant the decision to skip a Microsoft account:
- Corporate Environments: Organizations aiming for controlled IT environments may prefer local setups to manage all settings.
- Shared Spaces: In family or shared device scenarios where accounts may not be necessary or desirable.

Prerequisites
System Requirements
Before proceeding, ensure your setup meets:
- Running a necessary version of Windows 10.
- Admin privileges on the PC, which may be a requirement for executing certain commands.
- A network connection may be optional but can facilitate further steps.
Tools and Applications
The primary tool for this task is the Command Prompt (CMD):
- To open CMD as an Administrator: Search for “cmd” in Windows, right-click on the Command Prompt, and select "Run as Administrator". Elevating privileges is essential to execute system-level commands effectively.

Step-by-Step Guide to Skipping Microsoft Account Setup Using CMD
Accessing Command Prompt
Starting with Command Prompt is crucial. This is how you can access it:
- Search for CMD: In the Windows search bar, type “cmd”.
- Run as Administrator: Right-click on the search result and choose “Run as Administrator”.
Running commands with elevated privileges allows you to modify system settings and add new accounts, which is a vital step in our process.
Command to Bypass Microsoft Account
To create a local account and skip the Microsoft account setup, you’ll need to execute a specific command. Here's how:
net user LocalUser password /add
In this command:
- `LocalUser` is the username of your choice.
- `password` is where you define your desired password.
This command creates a new user account with the specified username and password, thereby establishing a local user environment on your Windows 10 machine.
Enabling Local Account
Next, it's necessary to grant the new local user administrative privileges. Execute the following command:
net localgroup administrators LocalUser /add
This step is crucial because it assigns the new user administrative rights, allowing them to modify settings and install applications on the machine without restrictions.
Setting Up Without Microsoft Account
When you proceed through the Windows installation process:
- Skip Microsoft Account Setup: At the account creation screen, simply input the local account credentials you created.
- Ignore Prompts: Make sure to choose options that favor local setups instead of the Microsoft account, which may include checking for “Offline Account” options if prompted.
This step solidifies your decision to maintain a local account setup, creating an efficient Windows environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Errors Encountered While Using CMD
While using CMD, you may encounter various error messages. Here are common examples along with their resolutions:
- “Access Denied”: Ensure you’re running CMD as Administrator.
- “User already exists”: This implies the username you’re trying to create is already in use. Try a different username or adjust the existing account.
Fallback Options
In cases where CMD doesn’t work as expected, consider these alternative approaches:
- Creating Users through Settings: You can navigate to Settings > Accounts > Family & other users to set up a local account.
- Using PowerShell: Another powerful tool, PowerShell, can also be used with similar commands to create users.
Conclusion
Utilizing the command line to skip the Microsoft account during Windows 10 setup can yield numerous advantages, emphasizing user privacy and enhancing simplicity. By following the outlined steps, you can successfully establish a local account, taking full control of your computing experience.

Additional Resources
Useful CMD Commands for Windows 10
While you focus on skipping Microsoft account setups, it’s helpful to familiarize yourself with other beneficial CMD commands, such as:
- `ipconfig`: Displays network configuration settings.
- `chkdsk`: Checks the disk for errors and repairs them.
- `sfc /scannow`: Scans system files for corruption.
References and Further Reading
For an in-depth understanding, refer to Microsoft's documentation on account management and additional resources covering more advanced CMD usages. These can provide deeper insights and help improve your CMD command mastery.