To access the D drive in the Command Prompt (cmd), simply type the drive letter followed by a colon and press Enter.
D:
Understanding CMD and Drives
What is Command Prompt?
The Command Prompt, often referred to as CMD, is a powerful command-line interface in Windows. It allows users to execute commands to perform various tasks—ranging from file management to system configuration—without using a graphical interface. The key benefits of using CMD include:
- Speed and Efficiency: Commands can be executed faster than navigating through multiple Windows menus.
- Automation: CMD scripts can automate repetitive tasks, increasing productivity.
- Access to Advanced Functions: Some functions and settings are only accessible or manageable via CMD.
How Drives are Structured in Windows
In the Windows operating system, drives are labeled with letters (C, D, E, etc.). The C drive is typically the primary drive where the operating system is installed. The D drive often represents additional storage, such as a secondary hard drive, external drives, or recovery partitions.
Understanding the structure of drives is essential, as it allows users to easily access files and directories via CMD. When you know the letter of the drive you want to access (in this case, D), you can quickly navigate there.

Accessing the D Drive in CMD
Opening Command Prompt
To start using CMD and access the D drive, first, you need to open the Command Prompt. You can do this in several ways:
- Using the Start Menu: Type “cmd” in the search bar, and click on the Command Prompt app that appears.
- Run Dialog: Press `Windows + R` to open the Run dialog, type `cmd`, and press Enter.
Once you've opened CMD, you're ready to begin accessing the D drive.
Changing Directory in CMD to D
Syntax for Change Directory Command
The `cd` command, standing for "change directory," is used in CMD to navigate between folders. The basic syntax for changing directories is straightforward:
cd [directory path]
How to Change Directory to D Drive
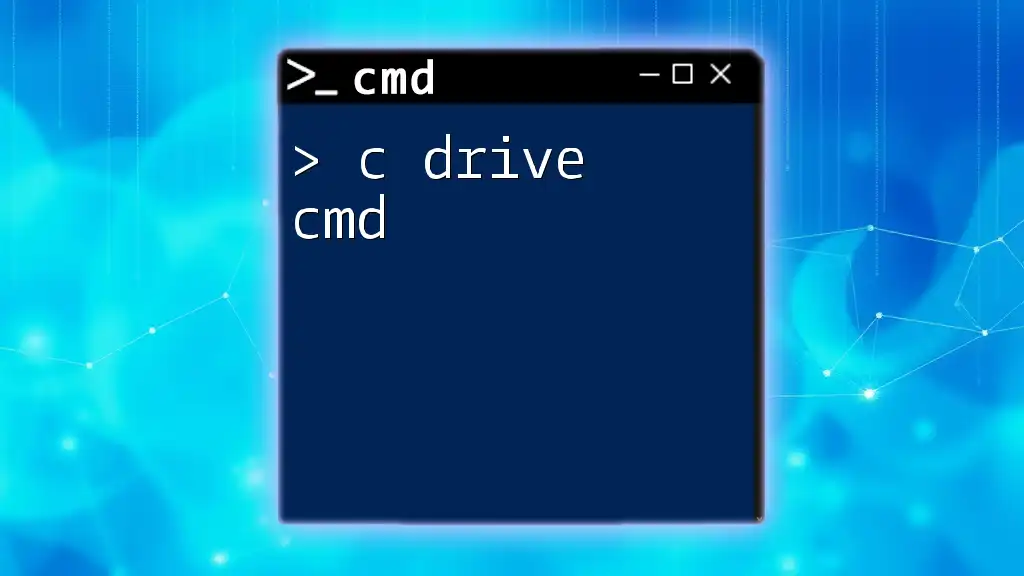
To access the D drive in CMD, you can simply type:
D:
Executing this command switches the focus of CMD from the current drive to D drive. It's important to understand that CMD operates within the context of the current drive, so switching directly helps in accessing all the folders and files located there.
Alternatively, you can use the `cd` command as follows:
cd D:\
This syntax explicitly indicates that you are changing to the root directory of the D drive.
Navigating Through D Drive's Directories
Listing Files and Folders
To view the contents of the D drive, you can use the `dir` command:
dir
When you execute this command, CMD lists all files and folders located in the current directory on the D drive. The output will include details such as file size, creation date, and folder names—all helpful for your navigation.
Changing Directories Within D Drive
To access specific folders within the D drive, use the `cd` command followed by the folder name. For instance, if you have a folder named “Documents” on the D drive, you would enter:
cd D:\Documents
If you need to move back up to the previous directory, the command is as simple as:
cd ..
This command takes you back one level in the directory hierarchy, making it easy to navigate through multiple folders.

Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Can't Access D Drive
Sometimes, users may encounter issues accessing the D drive in CMD. Here are common reasons and their solutions:
- Permissions: Ensure you have the necessary permissions to access files on the D drive. Running CMD as an administrator might help in these cases.
- Drive Recognition: If the D drive does not appear when you try to access it, check whether it’s correctly connected (if external) or properly formatted and allocated (if internal).
Tips for Efficient Navigation
To make navigation more efficient in CMD, consider these tips:
- Use Tab Completion: Pressing the Tab key while typing a folder name automatically completes it, saving time and reducing errors.
- Shortcuts: Use shortcut commands to assist; for instance, `cd` followed by folder names allows swift movement through deeply nested directories without needing the entire path.

Conclusion
Using CMD to access the D drive opens up a world of possibilities for file management. Through proper commands like `D:`, `cd`, and `dir`, you can quickly navigate your system without the drag of graphical interfaces. Regular practice of CMD commands will make you more adept and efficient in managing files and executing tasks directly.
Additional Resources
For those looking to deepen their understanding and expertise of CMD, various online resources, tutorials, and communities are available, offering comprehensive guides and video tutorials to further enhance your knowledge.