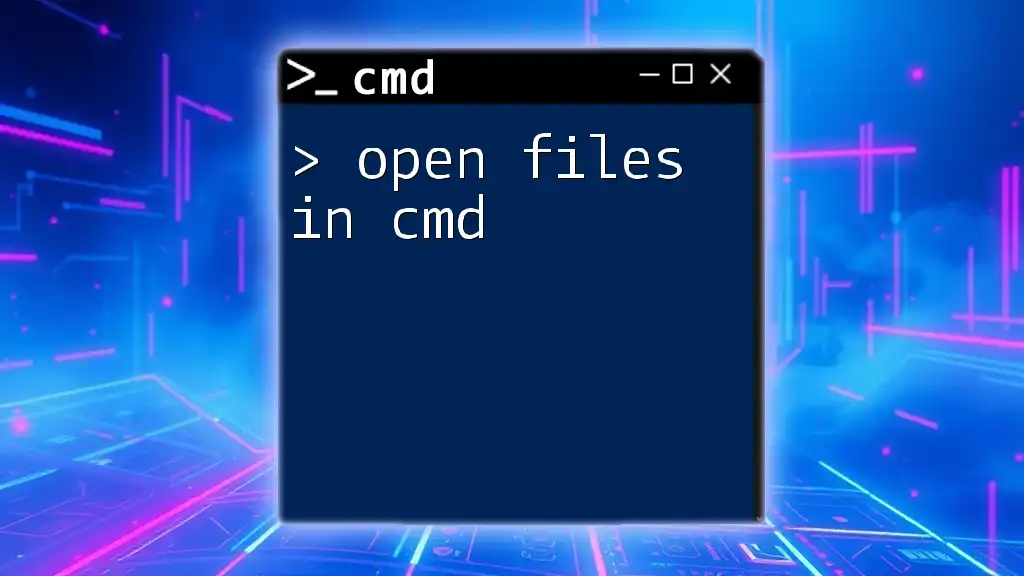
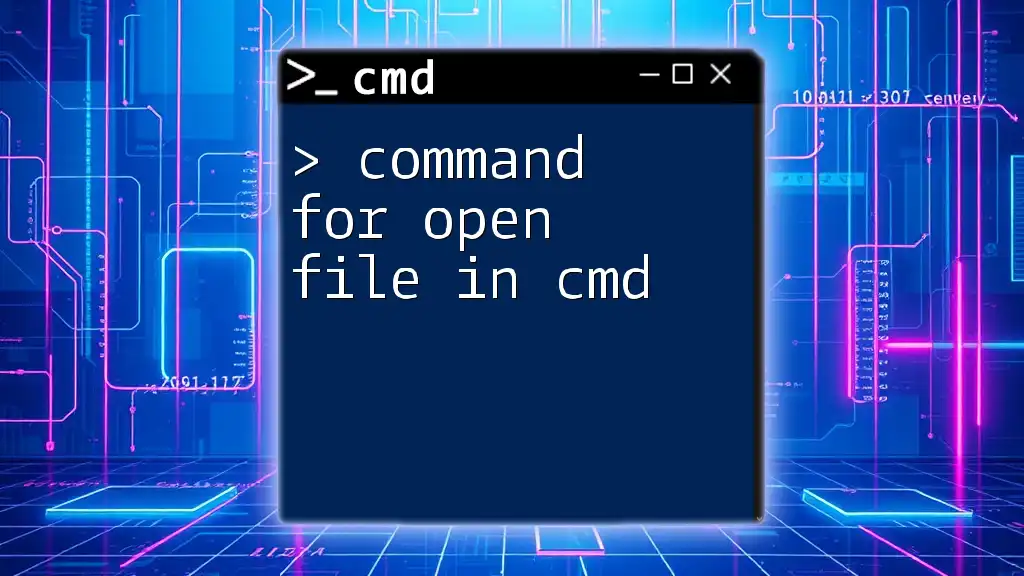
To open files in the Command Prompt (cmd), use the `start` command followed by the filename and file extension.
start example.txt
Understanding CMD and Its Capabilities
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful command-line interpreter found in Windows operating systems. It allows users to execute commands and automate tasks, offering a wide range of functionality that extends beyond basic file management. CMD is often used for troubleshooting, system administration, and running script files. Its capability to interface directly with the operating system makes it an invaluable tool for tech-savvy users.
Why Use CMD to Open Files?
Opening files via CMD has numerous advantages over the traditional graphical user interface (GUI):
- Speed and Efficiency: CMD allows you to quickly open files with a few keystrokes, without navigating through folders.
- Automation: You can script repetitive tasks, reducing the time spent on manual operations.
- Remote Management: CMD can be utilized in remote sessions, enabling control over machines without graphical interfaces.

How to Open Files in CMD
Navigating to the Desired Directory
Before you open a file, it's essential to be in the correct directory. This can be accomplished using the Change Directory Command (`cd`):
cd C:\Users\YourUsername\Documents
This command changes the current directory to your Documents folder, allowing you to perform operations related to the files contained within that location. Navigating effectively is crucial, as it sets the stage for successful file manipulation.
Basic CMD Commands to Open Files
Using `start` Command
The simplest way to open a file is by employing the `start` command, which launches the file with its associated application:
start filename.txt
For instance, to open a file named example.txt, you would type:
start example.txt
This command is versatile and can be used for various file types, making it a go-to option for many users.
Using `notepad` Command
If you're working specifically with text files and prefer to view or edit them in Notepad, you can utilize the `notepad` command directly:
notepad filename.txt
For example, to open a log file named logfile.log, you would enter:
notepad logfile.log
The `notepad` command is especially useful for quick edits and viewings of text-based documents.
Using `type` Command
If you simply want to see the contents of a file printed directly in the command line, use the `type` command. This command displays the content of a specified text file:
type filename.txt
For instance, to view a CSV file named data.csv, execute the command:
type data.csv
This is an efficient way of checking the contents without the overhead of launching an application.
Advanced Techniques for Opening Files with CMD
Opening Non-Text Files
Using `start` for Other File Types
The `start` command can also be employed to open non-text files such as images, PDFs, and spreadsheets. For example:
start image.jpg
start document.pdf
When you execute these commands, the system identifies the associated applications for these file types and opens them accordingly. This versatility allows for a seamless workflow.
Specifying File Paths
Using Absolute and Relative Paths
If the file you wish to open is located in a different directory, you can specify its path. Understanding absolute and relative paths is fundamental:
- Absolute Path: This is the complete path to the file, starting from the root directory:
start C:\Users\YourUsername\Pictures\photo.jpg - Relative Path: This references a file based on your current directory:
start ..\Documents\example.docx
Utilizing either method allows you to target files accurately.

Error Handling
Common Errors and Their Solutions
Even experienced users may encounter errors when opening files in CMD. Here are a couple of common issues:
-
File Not Found Error: If the file path or name is incorrect, CMD will generate an error message indicating the file cannot be found. Ensure you verify the file's existence and the accuracy of your commands.
-
Access Denied Error: This may occur if you lack the necessary permissions to open the file. Running CMD with administrator privileges may resolve the issue.
Tips for Efficient Use of CMD to Open Files
Keyboard Shortcuts and Automation
To enhance productivity, familiarize yourself with useful shortcuts within CMD. These can drastically reduce the time spent typing commands. Consider automating repetitive tasks by including commands in scripts, allowing for single-command execution instead of multiple input lines.
Creating Batch Files
Batch files are an excellent way to streamline the process of opening multiple files with a single command. A simple example of a batch file that opens two files could look like this:
@echo off
start file1.txt
start file2.docx
By saving this script in a `.bat` file, you can execute it whenever you need to open those files, saving considerable time and effort.
Conclusion
Mastering how to open files in CMD can significantly enhance your efficiency and capabilities in managing documents. With the techniques explored in this guide, from using basic commands to creating scripts for automation, you are now equipped to handle file operations with confidence. Take the time to practice and explore additional CMD functionalities to further solidify your command-line skills.