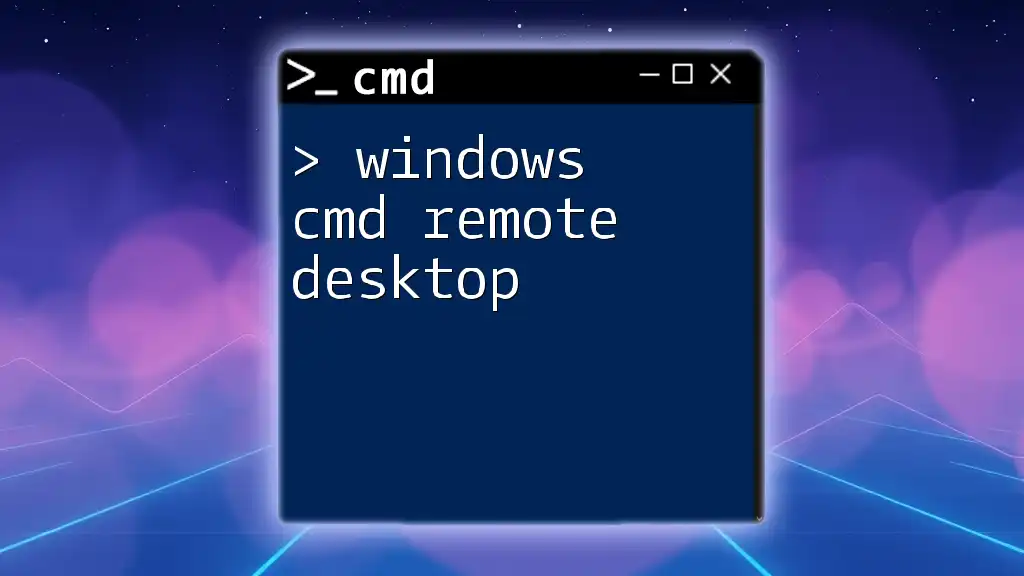
You can start a remote desktop session directly from the command prompt using the following command:
mstsc /v:<RemoteComputerName>
Replace `<RemoteComputerName>` with the hostname or IP address of the remote machine you want to connect to.
Understanding Remote Desktop
What is Remote Desktop?
Remote Desktop is a technology that allows you to connect to a computer or virtual machine from another location, enabling remote management and control. This capability is particularly beneficial for IT administrators, remote workers, and anyone needing quick access to resources without being physically present.
Key Components of Remote Desktop
- Remote Desktop Client: This is the software you use on your local machine to initiate the connection. On Windows, the built-in Remote Desktop Connection (often referred to as `mstsc`) serves this purpose.
- Remote Desktop Server: This is the target machine receiving the connection. It needs to have Remote Desktop enabled to accept inbound connections.
- Basic Requirements: To use RDP, ensure both machines are running compatible versions of Windows and are configured to allow remote connections. Also, verify that network connectivity is stable.

Setting Up Your Environment
Ensuring Remote Desktop is Enabled
Before you can start Remote Desktop from CMD, it's essential to confirm that Remote Desktop is enabled on the target machine. Here's how to do it:
- Open System Properties by right-clicking on This PC and selecting Properties.
- Click on the Remote settings link.
- In the Remote tab, ensure Allow remote connections to this computer is checked.
- Note: If you're using a professional or enterprise version of Windows, you will also need to ensure that the “allow only connections from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication” is selected for better security.
User Permissions
To access another machine remotely, the user must have permission. This usually involves:
- Creating user accounts on the target machine for those who need remote access.
- Ensuring that the connecting user is part of the Remote Desktop Users group on the server's user settings.

Launching Remote Desktop from CMD
Introduction to CMD and RDP
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool in Windows that allows users to execute commands and scripts. Using CMD to launch Remote Desktop can streamline the process, especially for those who prefer command line operations over graphical interfaces.
Basic Command to Launch Remote Desktop
The primary command used to start Remote Desktop from CMD is:
mstsc /v:hostname
In this command:
- `mstsc`: This is the command that invokes the Remote Desktop Client.
- `/v:hostname`: This parameter specifies the remote computer you want to connect to, where hostname can be either the IP address or the DNS name of the target machine.
Examples of Using CMD for RDP
Example 1: Connecting to a remote machine
For instance, connecting to a machine with the IP address `192.168.1.2` can be executed as follows:
mstsc /v:192.168.1.2
Upon executing this command, the Remote Desktop window will open, prompting for user credentials if everything is correctly set up.
Example 2: Connecting with a specific user account
If you wish to specify the username directly in the command, you can use the `/user` parameter as shown below:
mstsc /v:hostname /user:username
By inputting the username, you simplify the login process, but you will still be prompted for the password.
Additional Command Options for RDP
Using the `/f` Parameter for Full-Screen Mode
To open Remote Desktop in full-screen mode immediately, add the `/f` parameter:
mstsc /v:hostname /f
This option enhances the viewing experience, particularly on larger monitors.
Using the `/span` Parameter for Multi-Monitor Setup
If you’re using multiple monitors and want the session to span across all of them, you can employ the `/span` parameter:
mstsc /v:hostname /span
This will extend the RDP session across all available screens, perfectly tailored for a multi-monitor setup.
Saving Connection Settings
To save the settings so you can use them later without re-entering parameters, use:
mstsc /s:MySavedConnection
It allows for quicker access, particularly useful for frequent connections to the same server.

Advanced Remote Desktop Commands
Command-Line Options for Customizing Connections
Beyond the basic commands, there are additional options you can leverage:
- `/edit`: Modify saved connection settings.
- `/multimon`: Optimizes the connection to work seamlessly with multiple monitors.
Creating a Batch File for Quick Connection
For frequent connections, creating a batch file can save time. To do this, follow these steps:
-
Open Notepad or any text editor.
-
Write the command you would typically use. For example:
@echo off mstsc /v:192.168.1.2 -
Save the file with a .bat extension, such as `ConnectToServer.bat`.
-
Running this batch file will execute the command, efficiently launching your Remote Desktop session.

Troubleshooting CMD Remote Desktop Issues
Common Errors and Solutions
When attempting to start Remote Desktop from CMD, you might encounter several common issues, including:
- `Unable to connect`: Ensure that Remote Desktop is enabled on the server, and the firewall is not blocking the connection.
- `User account not authorized`: Verify that the user has permission and is part of the Remote Desktop Users group.
Verifying Remote Connectivity
To troubleshoot and ensure your connection is functioning:
-
Use the `ping` command to check if the remote machine is reachable:
ping 192.168.1.2 -
You can also use `tracert` to see the route taken to reach the target machine, identifying any potential network issues:
tracert 192.168.1.2
Conclusion
Utilizing CMD to start Remote Desktop offers a streamlined and efficient way to connect to remote machines. Whether you're an IT administrator managing networks or a remote worker needing quick access, this method enhances productivity and connectivity. Take the time to familiarize yourself with these commands and practice the provided examples to master the art of remote connections.
Additional Resources
For deeper insights, consider checking the official Microsoft documentation on RDP and CMD capabilities. Exploring tutorials specific to CMD can further enhance your skills and command over remote connections.