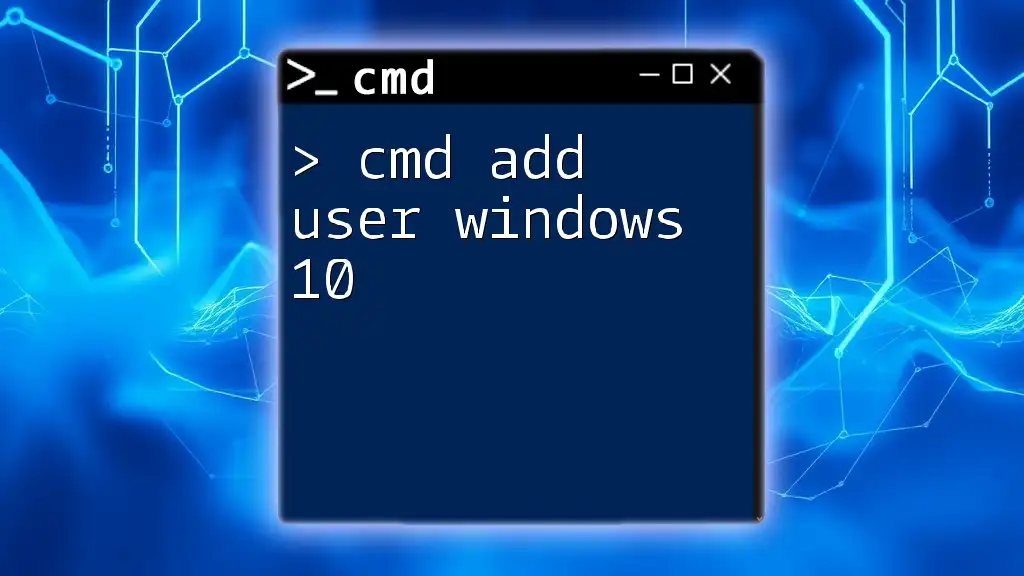
To change a user password in Windows 7 using the Command Prompt (cmd), you can use the following command syntax:
net user [username] [newpassword]
Replace `[username]` with the actual username and `[newpassword]` with the desired new password.
Understanding CMD and User Accounts
What is CMD?
CMD, or Command Prompt, is a command line interpreter found in Windows operating systems, including Windows 7. This powerful tool allows users to execute various commands to perform tasks ranging from file manipulation to system configuration. CMD dates back to the early days of PC operating systems and has evolved into an essential utility for both novice and advanced users.
Types of User Accounts in Windows 7
In Windows 7, there are primarily two types of user accounts that you may encounter:
-
Local User Accounts: These are accounts created on a single PC and are not linked to any external directory. They provide users with access to resources on that specific machine.
-
Administrator Accounts: These accounts have elevated privileges that allow users to make system-wide changes, manage other user accounts, and install software. Understanding the distinctions between these account types is crucial when changing passwords, as administrative privileges are often required.

Preparing to Change a Password via CMD
Accessing CMD
Before you can change a password, you must access the Command Prompt. Here's how:
-
Navigate to Start Menu: Click on the Windows icon in the bottom left corner.
-
Type 'cmd': As you type, you will see "cmd" appear in the search results.
-
Open CMD: Hit Enter. To run CMD as an Administrator, right-click the "cmd" result and select "Run as administrator." This is important for performing tasks that require higher privileges.
Confirming Your User Account
Once you have CMD open, the next step is to confirm your user account. Use the following command to display your current user account details:
whoami
This command returns information about your currently logged-in username and the account's domain, helping you verify if you have the correct privileges to change the password.
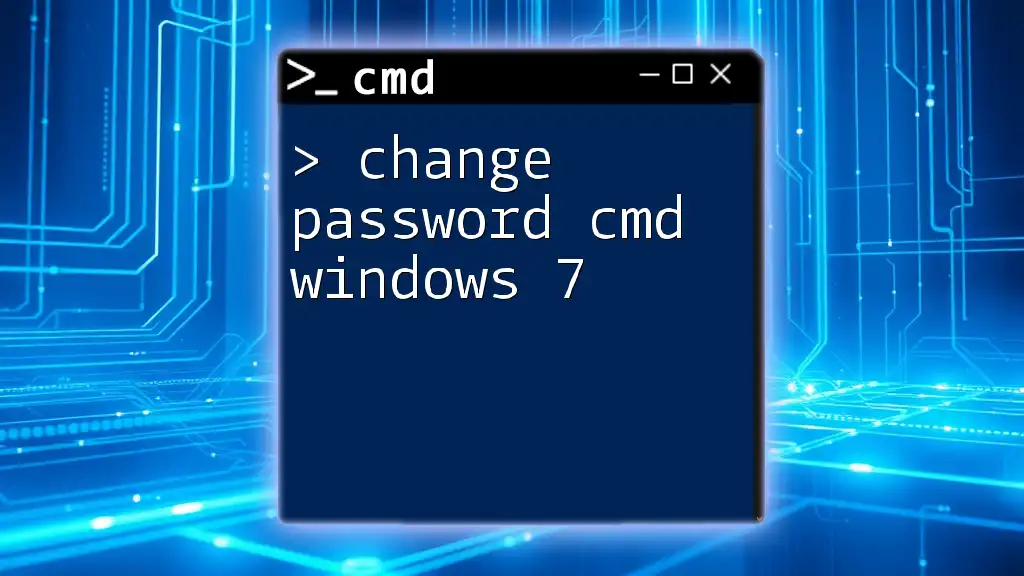
Changing the Password
Basic Command for Password Change
To change a user account password via CMD, you will utilize the `net user` command, which is designed for managing user accounts. The basic syntax is as follows:
net user [username] [newpassword]
- net user: This command is used for user management in Windows.
- [username]: Replace this with the actual username of the account for which you want to change the password.
- [newpassword]: Set this to the desired new password.
Example Walkthrough
Let’s go through a practical example of changing a password. Suppose the username is `JohnDoe`, and you want to set the new password to `NewSecurePassword123`. You would type:
net user JohnDoe NewSecurePassword123
Upon execution, if successful, you will see a message indicating that the command completed successfully. This straightforward process can significantly enhance user account management efficiency.
Handling Common Errors
Even experienced users may encounter errors while using CMD to change passwords. Here are a few common ones and their solutions:
Error: Access Denied
If you encounter the message "Access is denied," it typically indicates that you lack the necessary administrative privileges. Ensure that you have opened CMD as an Administrator. If still denied, check if you are logged in as an Administrator or if you're trying to change passwords of accounts that your user cannot manage.
Error: User Not Found
The "User not found" error suggests that the specified username does not exist. To avoid this problem, use the following command to list all local user accounts:
net user
This command will display a list of all accounts, allowing you to confirm that the username is correct before proceeding with the password change.

Additional Tips and Best Practices
Best Practices for Creating Strong Passwords
Creating a strong password is crucial for maintaining account security. Here are some essential tips:
- Length: Use at least 12 characters.
- Complexity: Incorporate numbers, symbols, and both uppercase and lowercase letters.
- Unpredictability: Avoid easily guessable information like birthdays or common phrases.
For example, a strong password might look like: `s7tR@ng3!P@ssw0rdExample`.
Regular Password Updates
Updating passwords regularly strengthens your security posture. Best practices suggest changing passwords every 3 to 6 months, depending on your security requirements. This practice helps mitigate risks associated with potential security breaches.
Alternative Methods for Changing Passwords
Using Control Panel
For those who prefer GUI over CMD, you can change your password via the Control Panel. Navigate to User Accounts and select your account. Look for an option to change your password, then follow the prompts.
Using Local Users and Groups
Another method involves using the Local Users and Groups management console. To access it, open the Run dialog by pressing `Win + R`, type `lusrmgr.msc`, and hit Enter. You can find your user accounts listed here, right-click on the account, and choose `Set Password`. Follow the instructions to complete the process.

Conclusion
Utilizing CMD for password management in Windows 7 is a valuable skill that can streamline system administration tasks. By mastering commands like `net user`, you can quickly change passwords, maintain account security, and enhance your overall computer literacy. Practice these commands to become adept at managing user accounts effectively.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I change passwords for other users with CMD?
Yes, if you have administrator privileges, you can change passwords for other users on the same computer by specifying the username in the command.
What if I forget my own password?
If you forget your password, you may need to use password recovery options, reset disks, or boot into safe mode to regain access.
Is CMD password change secure?
While changing passwords via CMD is secure provided you follow best practices and use strong passwords, remember to always run the Command Prompt with administrative privileges to prevent unauthorized changes.